一、Http响应与请求
HTTP是一种客户端-服务器协议,通信的双方分别是客户端和服务器。客户端发送HTTP请求,服务器接收并处理请求后返回HTTP响应。
1、Http请求
HTTP请求由请求行、请求头部、空行和请求数据(如POST请求时的表单数据)组成。
请求行包含请求方法、请求的URL和协议版本。常见的请求方法包括GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等。
请求头部包含关于客户端和请求的其他信息,如User-Agent、Accept、Content-Type等。
空行用于分隔请求头部和请求数据。
请求数据通常用于POST请求,包含提交的数据。
请求示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 POST /api/users HTTP/1.1 Host: www.example.com User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 Accept: application/json Content-Type: application/json Content-Length: 27 { "name": "John", "age": 30 }
请求行 :POST /api/users HTTP/1.1
请求头 :包含Host、User-Agent、Accept、Content-Type、Content-Length等
空行 :请求头和请求体之间的空行
请求体 :JSON数据
2、Http响应
HTTP响应由状态行、响应头部、空行和响应数据组成。
状态行包含协议版本、状态码和状态消息。状态码指示了请求的处理结果,如200表示成功,404表示未找到资源,500表示服务器内部错误等。
响应头部包含服务器和响应的其他信息,如Server、Content-Type、Content-Length等。
空行用于分隔响应头部和响应数据。
响应数据包含服务器返回的数据,如HTML、JSON等。
假设服务器返回一个简单的HTML页面,响应可能如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Sun, 02 Jun 2024 10:20:30 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu) Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 Content-Length: 137 Connection: keep-alive <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Example Page</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello, World!</h1> <p>This is a sample HTML page.</p> </body> </html>
状态行 :HTTP/1.1 200 OK
响应头 :包含Date、Server、Content-Type、Content-Length、Connection等
空行 :响应头和响应体之间的空行
响应体 :包含HTML代码
3、状态码
HTTP状态码指示了服务器对请求的处理结果。常见的状态码包括:
1xx:信息响应 ,表示请求已接收,继续处理。2xx:成功 ,表示请求已成功被服务器接收、理解、并接受。3xx:重定向 ,表示需要进一步操作以完成请求。4xx:客户端错误 ,表示服务器无法处理请求。5xx:服务器错误 ,表示服务器在处理请求时发生了错误。
二、Requests库
Python的Requests库是一个非常强大且易于使用的HTTP库。
在使用之前,需要先安装Requests库:pip install requests
1、发起GET请求
GET请求用于从服务器请求数据。使用Requests库发起GET请求非常简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 import requestsresponse = requests.get('https://news.baidu.com' ) if response.status_code == 200 : print (response.text) else : print (f"请求失败,状态码:{response.status_code} " )
2、发起POST请求
POST请求用于向服务器提交数据。例如,需要登录的网站通常使用POST请求提交用户名和密码。使用Requests库发起POST请求的方法如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import requestsdata = { 'username' : '123123123' , 'password' : '1231231312' } response = requests.post('https://passport.bilibili.com/x/passport-login/web/login' , data=data) if response.status_code == 200 : print (response.text) else : print (f"请求失败,状态码:{response.status_code} " )
3、处理请求头
在有些网站(例如豆瓣),不让爬虫有反爬取机制,需要设置HTTP请求头和参数,来伪装成浏览器通过身份验证。
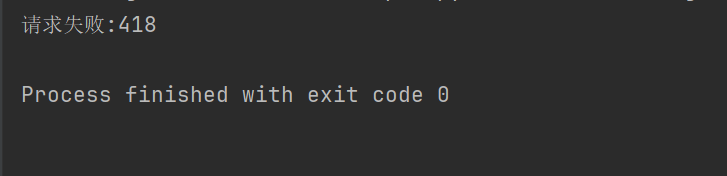
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 import requestsresponse = requests.get("https://movie.douban.com/top250" ) if response.ok: print (response.text) else : print ("请求失败:" + str (response.status_code))
例如,上面的代码,没有设置请求头,豆瓣就拒绝让我们访问。
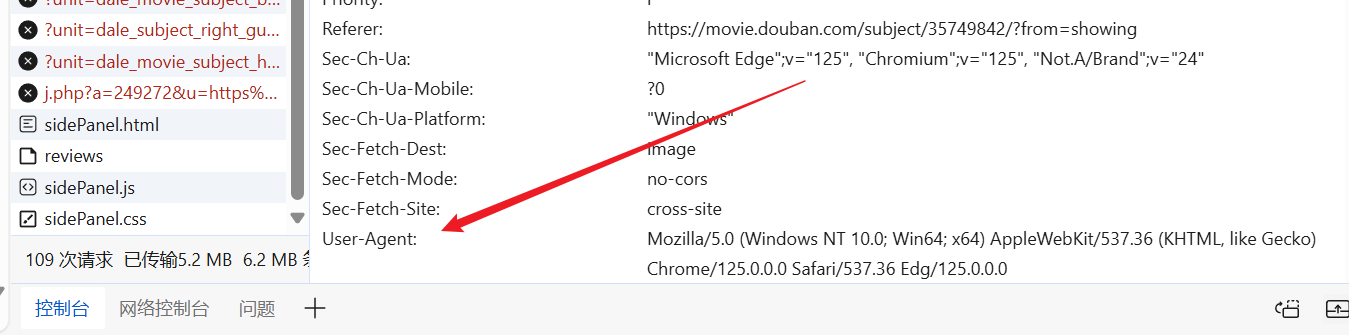
我们可用随便进入网站,随便找个现成的User-Agent,放到我们的请求头里。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import requestsheaders = { "User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/125.0.0.0" } response = requests.get("https://movie.douban.com/top250" , headers=headers) print (response.text)
这样,就能访问豆瓣,并且获取该网页的内容了。
三、BeautifulSoup库
BeautifulSoup 是一个用于解析 HTML 和 XML 文档的 Python 库,尤其适用于从网页中提取数据。
在使用之前,需要安装BeautifulSoup 库:pip install beautifulsoup4
1、解析HTML文档
html.parser是Python内置的解析器,适用于大多数场景。以上面的豆瓣为例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupheaders = { "User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/125.0.0.0" } response = requests.get("https://movie.douban.com/top250" , headers=headers) html = response.text soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser" )
2、查找和提取数据
BeautifulSoup提供了多种方法来查找和提取HTML文档中的数据。
BeautifulSoup常用方法:
find(tag, attributes): 查找第一个符合条件的标签。find_all(tag, attributes): 查找所有符合条件的标签。select(css_selector): 使用CSS选择器查找符合条件的标签。get_text(): 获取标签内的文本内容。attrs: 获取标签的属性字典。
Ⅰ、查找单个元素
find方法用于查找第一个符合条件的元素。例如,查找页面中的第一个标题:
1 2 title = soup.find("span" , class_="title" ) print (title.string)
Ⅱ、查找所有元素
findAll方法用于查找所有符合条件的元素。例如,查找页面中的所有标题:
1 2 3 all_titles = soup.findAll("span" , class_="title" ) for title in all_titles: print (title.string)
Ⅲ、使用CSS选择器
select方法允许使用CSS选择器来查找元素。例如,查找所有标题:
1 2 3 all_titles = soup.select("span.title" ) for title in all_titles: print (title.get_text())
Ⅳ、获取元素属性
可以使用attrs属性获取元素的属性字典。例如,获取所有图片的URL:
1 2 3 all_images = soup.findAll("img" ) for img in all_images: print (img['src' ])
四、爬取豆瓣电影榜
电影标题:HTML的标签名是:span,指定元素的 class 属性是 title
评分:HTML标签是:span,指定元素的class属性是rating_num
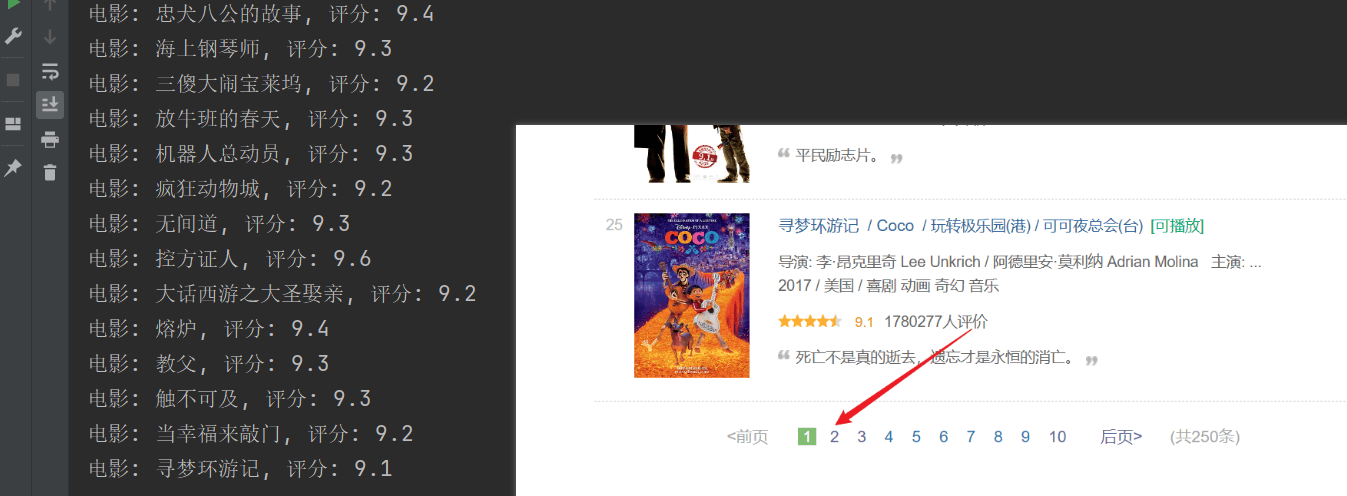
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupheaders = { "User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/125.0.0.0" } response = requests.get(f"https://movie.douban.com/top250" , headers=headers) html = response.text soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser" ) all_movies = soup.find_all("div" , class_="item" ) for movie in all_movies: titles = movie.find_all("span" , class_="title" ) for title in titles: title_string = title.get_text() if "/" not in title_string: movie_title = title_string rating_num = movie.find("span" , class_="rating_num" ).get_text() print (f"电影: {movie_title} , 评分: {rating_num} " )
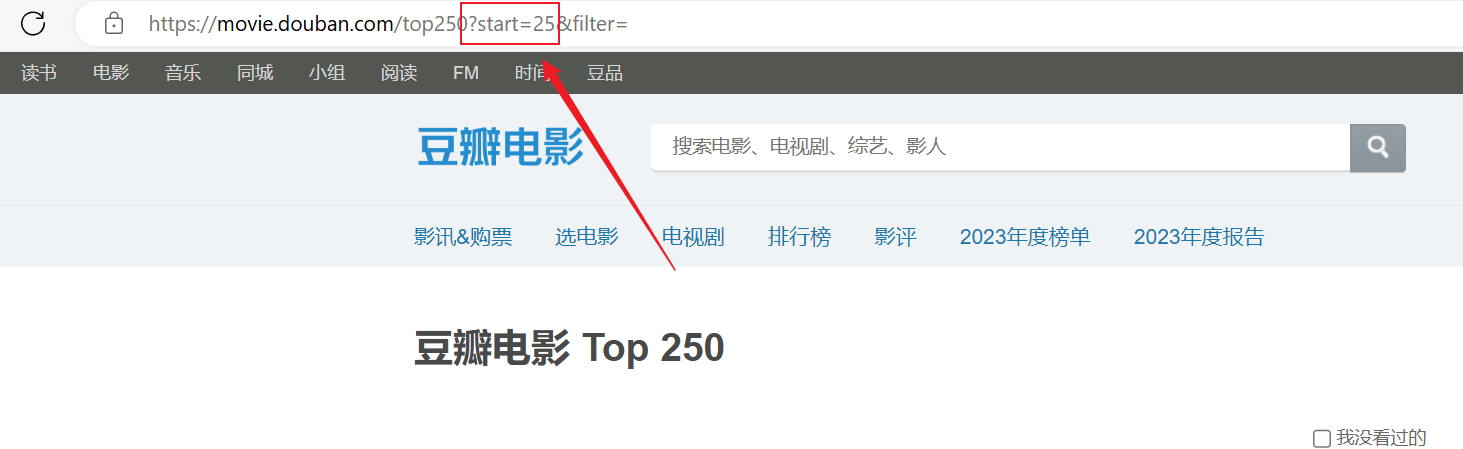
爬取成功了,但是爬取的内容只有第一页,后面的内容没有爬取成功。分析上面的url连接,每个页面通过URL中的start参数进行分页。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupheaders = { "User-Agent" : "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/125.0.0.0" } for start_num in range (0 , 250 , 25 ): response = requests.get(f"https://movie.douban.com/top250?start={start_num} " , headers=headers) html = response.text soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser" ) all_movies = soup.find_all("div" , class_="item" ) for movie in all_movies: titles = movie.find_all("span" , class_="title" ) for title in titles: title_string = title.get_text() if "/" not in title_string: movie_title = title_string rating_num = movie.find("span" , class_="rating_num" ).get_text() print (f"电影: {movie_title} , 评分: {rating_num} " )